The Consumer Price Index (CPI) average increasing rate is an indicator of the changes in the price level of a basket of goods and services that are typically purchased by consumers in country.
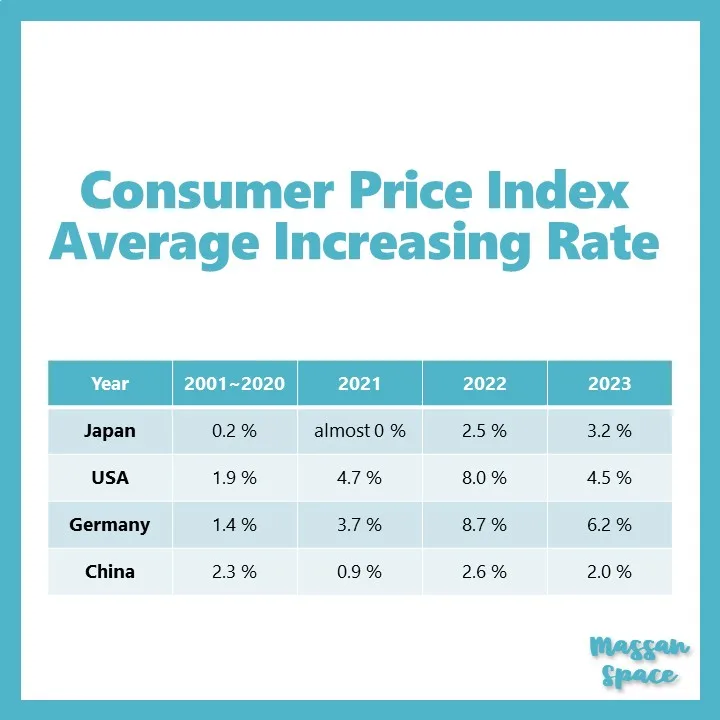
The below figure shows the comparison of CPI average increasing rate of Japan, US, Germany and China from 2021 to 2023. As a reference, a CPI average for 20 years from 2001 to 2020 is also plotted.
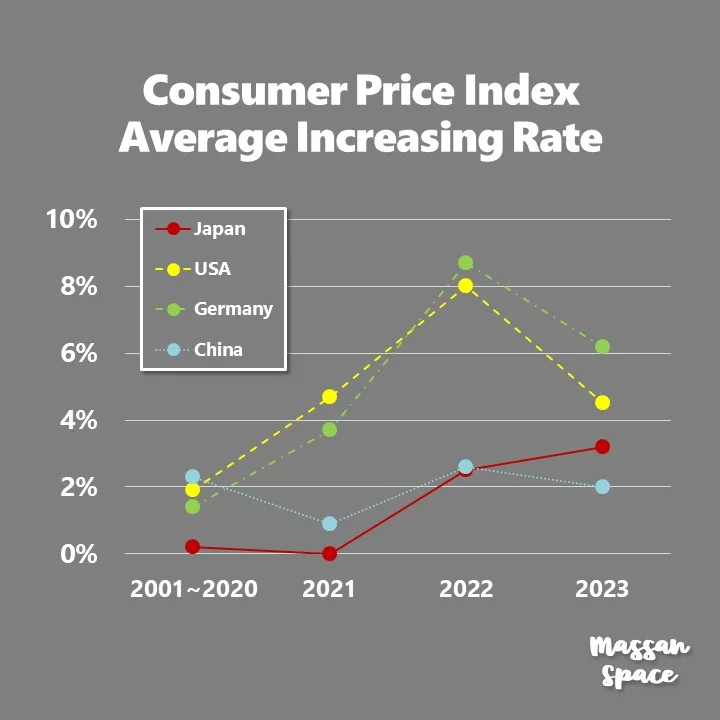
There are various factors that affect the CPI average increasing rate of theses countries.
1
The COVID-19 pandemic and vaccination progress have a significant impact on the economic activity and prices of different countries.
The pandemic has caused lockdowns, travel restrictions, supply chain disruptions, and reduced consumer spending, which have lowered the demand and inflation in some sectors.
However, the vaccination progress has helped to ease some of these effects and boost the economic recovery and consumer confidence in some countries.
However, the vaccination rates are uneven across countries, which creates inequality and uncertainty in the global economy.
2
The fluctuations in energy and food prices are another major factor that affects the CPI average increasing rate of these countries. Energy and food are essential goods that have a large weight in the CPI basket of most countries.
Therefore, changes in their prices can have a direct and significant impact on the overall inflation rate. For example, the surge in energy prices in 2022 was driven by the rebound in global demand, the limited supply from major producers, and the geopolitical tensions in some regions.
This has led to higher inflation and energy costs for consumers and businesses, especially in Europe. Similarly, the rise in food prices in 2022 was influenced by the adverse weather conditions, the higher transport and input costs, and the strong demand from China. This has increased the food insecurity and poverty for many people around the world.
3
The monetary and fiscal policies are also important factors that affect the CPI average increasing rate of these countries.
Monetary policy refers to the actions of central banks to influence the money supply and interest rates in an economy. Fiscal policy refers to the decisions of governments about taxation and spending.
Both policies can affect the aggregate demand and supply of goods and services in an economy, which in turn affect the price level and inflation.
For example, expansionary monetary and fiscal policies can stimulate economic growth and employment, but they can also create inflationary pressures if they are too loose or prolonged.
Conversely, contractionary monetary and fiscal policies can reduce inflation and debt, but they can also slow down economic activity and hurt financial stability if they are too tight or abrupt.


コメント